Summary
Summary IGCSE/GCSE Biology - Topic 09 Transport in Animals
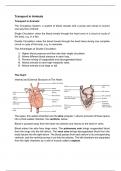
Complete set of IGCSE/GCSE Biology notes. Typed out, highly-detailed, contains plenty of diagrams, tables and illustrations for easy learning. Topics (01-21): 01 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms 02 Organization of The Organism 03 Movement in and out of Cells 04 Biolog...
[Show more]