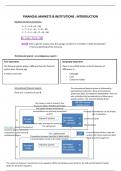
Summary
Samenvatting Financial Markets and Institutions
- Module
- Institution
This is a summary of the Financial Markets and Institutions course at the VUB taught by Professor Gielens and Professor Vandorpe. It is a combination of the Powerpoints and notes taken during all lectures.
[Show more]