Summary
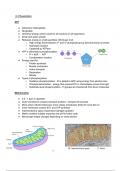
Summary Biology A2 level respiration notes (WJEC)
- Module
- Respiration
- Institution
- WJEC
Biology A2 level 3.3 respiration. These notes were formulated using class notes, the WJEC study guide and past papers. These notes helped me to achieve an A* at A level biology!
[Show more]