Lecture 1: MR modality overview
- MRI in vivo measurement of the brain
2 types of tissues that can be differentiated in MRI white and gray matter and CSF
4 types of MRI
- Structural MRI image
- Diffusion MRI fiber tracks
- Functional MRI (task)
- Functional MRI (at rest)
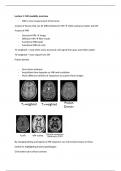
T1-weighted = most often used, structural. Get signal from gray and white matter
T2-weighted = more signal from CSF
Proton density
- Gross brain anatomy
- Acquisition time depends on SNR and resolution
- Many different varieties of sequences to acquire these images
By changing timing and signals of MR sequence can null certain tissues or flows
Useful for highlighting lesions/pathologies
Give better sub-cortical contrast
, By sensitising the sequence to different properties can detect other features of tissue:
- Swi/qsi, S= susceptibility, magnetic field changes due to iron contect and myelin
- MT: magnetisation transfer: bound or free water
- Veno/Angio grams; flow blood iron/contract agent
Structural MRI
- Tissue types GM, WM, CSF
- Cortical surfaces and thickness
- Sub cortical structure and shape (limbic system as well)
- Local Gray matter changes
These pictures based on water and fat density (proton density), T1 relaxation time, T2
relaxation time.
- Relaxation times depend on many things but are sensitive to micro-environment and
tissue type.
- Intensity is usually a complicated weighting of different factors
Structural MRI is NOT A DIRECT MEASURE. Not counting axons, cell bodies etc.
- Only indirect measures that are influenced by the tissues such as water and fat
- Not quantitative
- T1 and T2 values vary withing GM and WM
- Doesn’t distinguish bone from air
- Contrast poor in subcortical regions
- Single sequences may miss certain things completely might not be able to see a
tumour
- Artefacts and noise MRI easily affected by external factors
o Hardware related (contrast noise, how well can you differentiate between
tissues)
o Resolution and partial voluming
For analysis contrast to noise ratio (CNR), often most important
Hardware related bias:
- RF Bias (B1 inhomogeneity)
o Non-uniform RF field causes smooth variations in intensity
o Can sometimes become very larger
- MRI in vivo measurement of the brain
2 types of tissues that can be differentiated in MRI white and gray matter and CSF
4 types of MRI
- Structural MRI image
- Diffusion MRI fiber tracks
- Functional MRI (task)
- Functional MRI (at rest)
T1-weighted = most often used, structural. Get signal from gray and white matter
T2-weighted = more signal from CSF
Proton density
- Gross brain anatomy
- Acquisition time depends on SNR and resolution
- Many different varieties of sequences to acquire these images
By changing timing and signals of MR sequence can null certain tissues or flows
Useful for highlighting lesions/pathologies
Give better sub-cortical contrast
, By sensitising the sequence to different properties can detect other features of tissue:
- Swi/qsi, S= susceptibility, magnetic field changes due to iron contect and myelin
- MT: magnetisation transfer: bound or free water
- Veno/Angio grams; flow blood iron/contract agent
Structural MRI
- Tissue types GM, WM, CSF
- Cortical surfaces and thickness
- Sub cortical structure and shape (limbic system as well)
- Local Gray matter changes
These pictures based on water and fat density (proton density), T1 relaxation time, T2
relaxation time.
- Relaxation times depend on many things but are sensitive to micro-environment and
tissue type.
- Intensity is usually a complicated weighting of different factors
Structural MRI is NOT A DIRECT MEASURE. Not counting axons, cell bodies etc.
- Only indirect measures that are influenced by the tissues such as water and fat
- Not quantitative
- T1 and T2 values vary withing GM and WM
- Doesn’t distinguish bone from air
- Contrast poor in subcortical regions
- Single sequences may miss certain things completely might not be able to see a
tumour
- Artefacts and noise MRI easily affected by external factors
o Hardware related (contrast noise, how well can you differentiate between
tissues)
o Resolution and partial voluming
For analysis contrast to noise ratio (CNR), often most important
Hardware related bias:
- RF Bias (B1 inhomogeneity)
o Non-uniform RF field causes smooth variations in intensity
o Can sometimes become very larger