Unit 11: Genetics and Genetic engineering
A: Understand the structure and function of nucleic acid to describe gene expression and the
process of protein synthesis
Structure and function of nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are type of large biomolecules and they are universal meaning they occur in all living
organisms. Nucleic acids are formed from monomers known as nucleotides. The chemical reaction
that joins nucleotides together is called a condensation reaction. The nucleotide has five bases:
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil. Adenine and guanine are purines due to them only
having a double ring structure and cytosine, thymine and uracil are pyrimidines due to them having a
single ring structure.
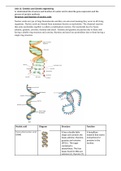
Nucleic acid Diagram Structure Function
Deoxyribonucleic acid It has a double helix A hereditary
(DNA) shape and contains the material that stores
bases adenine, thymine, instructions for
guanine and cytosine proteins in the
(ATGC). The sugar nucleus.
contained is
deoxyribose. The four
bases found in DNA are
adenine (A), thymine (T),
, Unit 11: Genetics and Genetic engineering
A: Understand the structure and function of nucleic acid to describe gene expression and the
process of protein synthesis
cytosine (C), and guanine
(G).
Messenger ribonucleic They contain three bases Is made using DNA
acid (mRNA) and each base, also and has temporary
known as codon, instruction for cells
specifies an amino acid. in order to make
The sugar found in RNAs protein. They carry
are called ribose. genetic info from
The four bases found in nucleus to the
RNA are adenine, ribosome.
guanine, cytosine, or
uracil.
Transfer ribonucleic They are a clover leaf Transfers the amino
acid (tRNA) shape and have three acids to the protein
bases that join to the that is growing.
mRNA codon at a time.
The sugar found in RNAs
are called ribose. The
four bases found in RNA
are adenine, guanine,
cytosine, or uracil.
Ribosomal ribonucleic It is a single sphere Makes up the bulk
acid (rRNA) shape that contains of ribosomes. The
ribosomes made up from catalyst in
ribonucleic acid and ribosomes is the
protein which form RNA which enables
nucleoproteins. The assembly in
sugar found in RNAs are proteins.
called ribose. The four
bases found in RNA are
adenine, guanine,
cytosine, or uracil.
Small interfering SiRNA has double They help to
ribonucleic acid strands of RNA regulate gene
(siRNA) molecules and is long. activity by breaking
The sugar found in RNAs down or blocking
are called ribose. The mRNA or by causing
four bases found in RNA some genes to
are adenine, guanine, become
cytosine, or uracil. methylated.
DNA replication
Mitosis or meiosis takes place before replication. DNA defines every cell in the body and therefore
the division of cells plays a big factor in it. Replication happens in the S phase of interphase during
this cell cycle. The replication of DNA results in two new molecules of DNA to be made. These two
molecules are identical to each other. Each molecule has one old strand and one new strand. DNA
replication is important in the growth, repairing and reproduction of cells in an organism.