Working in Health and Social Care – unit 2
A – The roles and responsibilities of people who work in the
health and social care sector
A1 – the roles of people who work in the health and social care setting
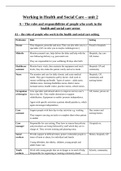
Profession Role Setting
Doctor They diagnose, prescribe and treat. They can also refer you to a Found in hospitals
specialist. (GP can refer you to maybe cardiologist etc.)
Midwife Monitor prenatal care, help deliver the baby and help with the Hospitals, day care
care following delivery e.g. post-natal care. GP, homes
They are responsible for your wellbeing 28 days after birth
Healthcare Monitor basic vitals, they maintain the equipment and stock Hospitals GP and
assistant levels, they also make the patient comfy and serve meals community
Nurse The monitor and care for daily chronic and acute medical Hospitals, GP,
needs. They give treatments said by doctor. And work to community and
restore wellbeing and health. Types of nurses – adult nurse, nursing homes
children nurse, learning disabilities nurse, district nurse,
neonatal nurses, health visitor, practice nurses, school nurses.
Occupation Give specialist and tailored advice to improve service user’s GP, homes, prison etc.
al therapist day to day life. They enable alterations to support
rehabilitation. Equipment to enable/ promote independence.
Agree with specific activities a patient should partake in, which
again encourages independence.
Care Support people with their day-to-day activities e.g. washing Day centres and
assistant nursing homes.
They support carrying out tasks or complete them when patient
is unable.
Care Responsible for care setting. They have to ensure that policies Hospitals etc
manager and procedures are being followed by staff which they are in
charge of. They oversee training and planning rotas.
Social Provide support in difficult times; protect vulnerable people in Homes, hospitals, GP.
workers times of harm or abuse, for individual and family
Young offenders, the elderly, children, young people and
adults foster care
Youth Work with young people that are in danger or in need of help. Schools, community.
workers Responsible for organising or running community-based
, projects.
Support Work with families or individuals in agencies or such. Support Homes etc.
worker family according to illness disability or other issues. Help
individuals with their daily tasks.
A2 – The responsibilities of people who work in the health and social care
settings
● Following policies and procedures
● Healing and supporting
● Enabling rehabilitation
● Providing equipment and adaptations
● Proving personal care
● Supporting routines of service users
● Assessment and care and support planning
THE SEVEN CARE VALUES
● Promoting effective communication and relationships.
● Promoting anti-discriminatory practise (including policies and codes of practise).
● Maintaining confidentiality of information.
● Promoting and supporting individual’s rights to dignity, independence, empowerment, choice
and safety.
● Acknowledging individual’s personal beliefs and identity and respecting diversity.
● Protecting indi
● viduals from abuse
● Providing individualised care.
Policies and procedures
They must be followed I order to ensure that the care provided meet the service user’s needs.
They aim to ensure that all staff works according to the laws and the highest professional standards as
well as guarantee their safety. E.g. health and safety policy and the safeguarding policy
Prescribing medication
Traditionally, it is a doctors role however, some nurses can undergone additional to become nurse
prescriber
Surgery
It is to support an individual’s recovery from the illness and other physical disorders. Care workers =
role to support people’s recovery from surgery. E.g. visits from district nurse OT (occupational
therapist) if necessary. Social workers may provide emotional support. Care worker practical help
Radiotherapy
Treatment using high energy radiations. Used to treat cancers but can be used to cure non- cancerous
diseases e.g. thyroid glands, some blood disorders. Patients need help from doctor for full healing GP
practices, for side effects e.g. itching peeling or blistering of the skin.
Organ transplant
, It is the movement of a body part or organ to or from a person. From a person to another (allograft)
from body part to another same body (autograft). It is to replace the damaged body or absent organs.
Commonly heart kidney, lungs, liver, pancreas and intestines. Done by skilled surgeons.
Supporting lifestyle changes
Changing daily routines and habits = damaging for health but can also be important for improvement
of the health of a person. E.g. exercising, healthy eating. This is done by practice nurses, GP practices
and district nurses.
Accessing support from specialist agencies
Age UK – supports older people and their health
Mind – supports people with mental health issues and brings awareness to it
Young minds – improving mental health of young people
(RNIB) royal national instate of blind people - support people affected by sight lose or people
partially blind
Alzheimer’s society – info to support for people with dementia or fam suffering from this, raise
awareness.
Enabling rehabilitation
Enable person to recover from accident or mental illness to fulfilling life, support from a
physiotherapist, occupational therapist, councillors and psychotherapist
A3 – Specific responsibilities of people who work in the health and social
care settings Discriminations is when people are treated
unfairly or unequally and therefore
Promoting anti-discriminatory practices experience prejudice.
ANTIDISCRIMINATORY PRACTICES :
- Accessible signage
- Leaflets in many language
- Access to buildings
- Longer appointment for people with learning disabilities
- Policies such as anti-bullying in schools.