2
Chiamaka Udoye
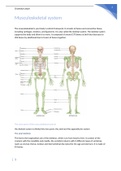
Musculoskeletal system
The musculoskeletal is your body’s central framework. It consists of bones and connective tissue,
including cartilages, tendons, and ligaments. It is also called the skeletal system. The skeletal system
supports the body and allow it to move. It composed of around 270 bones at birth but decrease to
206 bones by adulthood due to fusion of bones together.
The main parts of the musculoskeletal system
the skeletal system is divided into two parts: the axial and the appendicular system
The axial skeleton
This forms the longitudinal axis of the skeleton, which runs from head to feet. It consists of the
cranium with the mandible and maxilla, the vertebral column with it different types of vertebrae
(such as cervical, thorax, lumbar and intervertebral disc) plus the rib cage and sternum. It is made of
81 bones.
1
, 2
Chiamaka Udoye
The appendicular skeleton:
This is the part of the skeleton of the vertebrates consisting of bones supporting the appendages.
They are composed of bones of the lower and upper limb, together with the shoulder girdle and
pelvic girdle. The appendicular skeleton is made of 126 bones.
2
, 2
Chiamaka Udoye
What are bones made up from
Bones are made up of connective tissue with a framework protein called collagen and are reinforced
with mineral called calcium phosphate that makes the bone hard and strong. Bones store calcium
and release some into the bloodstream when it is needed by other parts of the body.
The periosteum
It is a membranous tissue that cover the surface of your bone. In the periosteum there are many
blood vessels, lymphatic vessel and nerve fibre which enter the bone tissue through a special canal.
The periosteum is made up of two distinct layers: the outer layer that consist of dense connective
tissue and the inner layer that consist of osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
The compact bone
The hard-external layer of all bone tissue is called compact bone also known as the cortical bone.
They are hard, heavy and have a smooth surface. They contain the yellow bone marrow and form a
protective shell around the spongy bone. It is covered by a periosteum from the outside. A good
example is all the long bone such as arm and legs. The compact bone is formed from a number of
osteons also known as the haversian system which are the fundamental unit of much of the compact
bone. Each osteon contains several different cells used for the maintenance of the bone which
include the osteocytes and the osteoblast. Inside each osteon houses a space which is called the
central canal which has the blood supply vessel and nerves. The compact bone is main structure for
support, protection and moment in the body and can also be used to store calcium and release it to
the body when needed. It can also supply strong mechanical lever against muscle which can create
movement. The compact bone accounts for 80% of the body weight.
The spongy bone
The spongy bone also known as the cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is an osseous tissue found
in the middle of the bone and it composed the inner layer of the bone. It is usually found in the at
the ends of long bones, the skull, the ribs, and the vertebrae with the compact bone surrounding it.
The spongy bone is softer, weaker, and more flexible than the compact bone. The primary unit of the
spongy bone is called the trabecular which forms the lattice-like matrix of the bone which houses the
red bone marrow and blood vessels. The blood vessel travel from the compact bone the spongy
bone with material used to create blood cell. Then spongy bone is composed of cells called the
osteocytes and are positions closed to the blood vessels so that they can take nutrients and expel
waste though a space called the canaliculi. The spongy bone is converted to a compact bone though
a process called the osteoblast which deposit new bone material around the matrix of the bone. The
spongy bone is used for more active function of the bone such as blood cell production and ion
exchange. It accounts for 20% of bone weight
The bone marrow
The bone marrow is a soft spongy tissue that is found in the centre of most bones. There are two
types of bone marrow which are the redbone marrow also known as the myeloid tissue and yellow
bone marrow also known as the fatty tissue. The red bone marrow consists a highly vascular fibrous
tissue which contain the hematopoietic stem cell that can become red blood cell, white blood cell
3
, 2
Chiamaka Udoye
and platelets. The yellow bone marrow is mostly made of fat and contain mesenchymal stem cell
that can become cartilages, fat, or bone cells.
Mineral use
When the protein in the cartilage matrix becomes ossified (turn to bone) if form crystal of mineral
calcium phosphate with magnesium, sodium, potassium ions that are deposited in the organic
collagen matrix. The mineral content found in bones gives it compressive strength while the collagen
fibre in the organic matrix gives it tensile strength. The calcium in bones can be used to store and
top of level of calcium ions in blood (for clotting) and muscles (for contraction)
Types of bones
Long bones: long bones are those that are longer than they are wider. The consist of a long tubular
shaft(diaphysis) and two bulky end (epiphyses) that are wider than the shaft. They are hard and
dense and provides structure and motility. This gives bones extra solidity at the joint where bones
articulate with one another they are mostly made of compact bone with spongy bone at the
epiphyses. Example are the tibia, femur, fibula, metatarsals, humerus, ulna. Etc
4
, 2
Chiamaka Udoye
Short bones: They are as long as they are wide. The structure it is to provide stability and some
movement with no loss of strength. It consists of spongy bone with a thin layer of compact bone.
They are found in the wrist ankle and kneecap. Example are the lunate, scaphoid, trapezoid,
capitate, etc
5