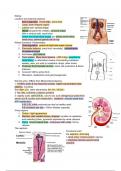
Kidney
Location and external anatomy
- 6cm in diameter, 11cms high, 3cms thick
- Large, bean-shaped organs
- Lateral side- convex shape
- Medial (towards the middle)- concave shape
- With a vertical cleft, renal hilum
Ureter and renal blood supply join kidney at the hilum,
renal sinus, adrenal glands sits on top
Kidney functions- Homeostasis
1. Osmoregulation, control of total body water volume
2. Electrolyte balance, body fluid ‘osmolality’, concentration
of solutes in blood
3. Acid-base (pH) balance
4. Toxic wastes, filters blood plasma (~200 L/day) supplied by
renal artery, no alternative means of excerpting metabolic
wastes; urea, uric acid or creatinine, drugs, other toxins
5. Produces Erythropoietin & renin, blood cell production & blood
pressure
6. Converts VitD to active form
7. Starvation, metabolism and gluconeogenesis
Normal urine- Differs from filtered blood plasma:
1- 91-96% water & rest dissolved solutes (higher concentration than
plasma), including:
Salt (Na+, Cl-), other electrolytes (K+, H+, HCO3-)
2- No cells, nutrients or plasma proteins
3- slightly acidic (pH 5.5-6.0), urea & Uric acid (nitrogenous waste from
amino acid & nucleic acid metabolism), creatinine (muscle waste from
ATP metabolism)
0.6L-2.6L urine produced per day by healthy adult
6-8 urinations per day (~350ml bladder capacity)
3 key regions
1. Cortex - light appearance
2. Medulla- dark reddish-brown, stripped, bundles of capillaries
and collecting tubes, pyramids separated by renal columns
3. Pelvis- funnel shaped tube, continuous with ureter, fed by
calyces
The nephron
Functional unit=
the nephron ~3cm long
1-renal artery crosses pelvis/ calyces
2-Interlobar arteries ascend renal
columns
, 3-afferent arterioles supply glomerular capillaries for plasma filtration at bowman’s capsule
4- efferent arterioles drain glomeruli
5- peritubular capillaries around PCT & DCT reclaim
reabsorbed substances
6- & vasa recta (straight vessels) in medulla parallel
to Loop of Henle, for water/ion exchange
Nephrons & vascular relations: peritubular & vasa
recta capillaries
Consider 3 main functions
1- filtration: between the
glomerulus/bowman’s capsule/ renal
corpuscle
2- reabsorption: by the proximal
convoluted tubule & Loop of Henle
3- secretion: by the distal convoluted
tubule
Plasma filtration
1- Blood enters glomerulus under pressure
- due to afferent arteriole
2- Glomerular endothelial wall is fenestrated
- plasma (not cells) forced through the pores
3- Bowman’s capsule podocytes wrap around the
glomerular capillaries
4- Plasma passes through filtration slits between
adjoining podocytes
- to enter lumen bowman’s capsule & then the
PCT