GASTROENTEROLOGY H+E:
Details
• Diarrhoea • Altered bowel habit: Red flags: ALARMS
/contraption Volume, smell, colour, freq, consistency,
• Weight gain/loss 1. Anaemia
• Appetite/Anorexia 2. Loss of weight
• Dysphagia • Solids/liquids/both (which came 1st) 3. Anorexia
• Intermittent + due to food = eosinophilic oesophagitis
• Odynophagia 4. Recent onset progressive
• Dyspepsia • Acid regurgitation (GORD) symptoms
History of • Abdominal Pain (Socrates) 5. Melaena/Haematemesis /
o CHRONIC + altered bowel habit = iBS Persistent vomiting
presenting • General • N +V + bloating + pruritus [Melaena (Exc. Fe tablets,
complaint • Fever + NS + fatigue peptic ulcers, small bowel
[DDD’s] • Urological • Storage: freq, vol., urgency, nocturia, incontinence bleed)]
[FUND WISE] • Infection: dysuria. Heamaturia, odour 6. Swallowing difficulty
• Gynaecological • PV bleeding: menorrhagia, post-coital /dysphagia
• PV discharge (esp. >55 y.o., >4
• Pain: pelvic, dysmenorrhoea, dyspareunia weeks/relapsing)
• Pregnancy 7. Painless bleed = aortic
enteric fistula (AAA)
8. Painful bleed = fissure, IBD,
abscess
• Conditions: Previous H. pylori infections | gallstones | Diabetes| SCI/MS/Hirschsprung disease | Thyroid issue
Past MHx • Medications (calcium antacids, opiates, TCAs cause constipation)
[CHOMV • Surgeries - Abdominal (appendectomy, anaesthesia)
If ANAEMIA suspected, exclude:
STAVE] • Tests (exploratory) = (biopsies, tTg-IgA, colonoscopy, gastroscopy)
• Allergies? (e.g. to aspirin, NSAIDs, intravenous contrasts) 1. GI malignancy
• Home life/accommodation + partners + single (sex – condom?) 2. Fe deficiency or B12/Folate
• Occupation: HCW (hepatitis exposure) 3. Menorrhagia
Social Hx 4. Vwf Disease
• Tattoos & Illicit Drugs (injections)
[WHIT SADOM] 5. Upper GI bleed or peptic ulcer
• Smoking (pack years) + when did they quit
• Alcohol (CAGE questions) = ESSENTIAL 6. Coeliac disease/ IBD
• Family Hx of colon cancer (esp. family polyps) | IBS | Coeliac disease | H. pylori infections | pancreatitis
Family Hx • Hemolytic anemia or congenital hyperbilirubinemia = family Hx of jaundice, anemia, splenectomy or
cholecystectomy
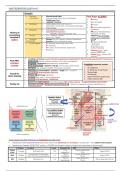
GORD/PUD
CHOLECYSTITIS PANCREATITIS
L3 -SUBCOSTAL
Xiphersternum AAA / SBO/ LBO
PYELONEPHRITIS
RENAL COLIC
L5-INTER-
TUBERCULAR
PLANE
APPENDICITIS
PREGNANT
Distended
Pubic symphysis bladder
Acute Abdominal Pain (Visceral vs. Peritoneal (somatic) Pain)
• Visceral pain (non-localised | focal) starts much earlier than peritoneal pain (localised – somatic pain – may radiate/referred pain)
• Visceral pain Creates “MIGRATORY” pattern ® DIVIDED into foregut, midgut or hindgut pain depending on blood supply
Division Location Level Somatic Pain SNS PSNS
Celiac T7-9 Greater splanchnic
Foregut RUQ and LUQ T12 Vagus (CNX)
trunk (epigastric) T5-9
to proximal 2/3 transverse T10-11 Lesser sphlanchnic
SMA Midgut L1 Vagus (CNX)
colon (Central/paraumbilical) (umbilical) T10-11
T12-L1 Least splanchnic
IMA Hindgut RLQ and LLQ L3 Pelvic splanchnic (S2-4)
(suprapubic) T12-L2
, OTHER MAJOR SYMPTOMS IN DETAIL:
• Involuntary explosive ejection of stomach contents through mouth
Colour Location
Bile (green-yellow) SBO, duodenal atresia,
VOMITING Faeculent (brown) Small or large bowel obstruction
“contents Coffee ground Fe tablet, red wine & coffee ingestion
frequency
Undigested Food Gastric outlet obstruction (level of pylorus)
amount
Red blood/ • Upper GI Bleeding or maligancy(any bleeding proximal to Duodenal-Jejunal flexure)
Haematemesis • Multiple episode of vomiting? = Mallory-Weiss Tear
Chronic unexplained • Pregnancy (AM sickness), Bullemia, Alcoholism or drugs (e.g. digoxin, opiates, chemo)
DDx KEY FEATURES
• Elderly> UWL > Anaemia (SOB, fatigue)
Colon cancer
• Melaena (Exc. Fe tablets, peptic ulcers, small bowel bleed)
• Acute diarrhoea
Gastroenteritis
• N+V
IBS • (1)abdominal cramping pain/bloating è relieved on defecation
• (2 + 3 ) Altered stool frequency + appearance® Fluctuate diarrhoea/constipation “toothpaste stools”
CHANGE OF (Rome IV criteria
– at least 2 of 3) • Anxiety/stress > Jaundice > Pruritus, lethargy
BOWEL HABIT • Steatorrhea [fat malabsorption]
(Wide range of o excl. pancreatic disease with lipase deficiency, OR use Investigations:
normal; of weight-loss drug - orlistat
3 x /day to once Coeliac disease • Assoc with: Anaemia, T1DM, Osteoporosis, autoimmune • Serology: Elevated tTG IgA
every 3 days) disease (e.g. thyroid), malignancy (e.g. lymphoma, small • Genetics: HLA DQ2/8 to EXCLUDE CD
intestinal carcinoma) • Gold standard = duodenal biopsy (x6)
• Abd discomfort (N+V, flatulence, cramping) •
“Have you noticed
your bowel habit • Bright red Blood (heamatochezia)/mucus in stool (exc. colon cancer, beetroot ingestion)
change? What • Abd pain + weight loss
happened?” o Crohn’s = affects entire GIT
IBD
o UC = affects only colon
(UC or crohn’s)
“Do you mean o Small bowel or Right colonic bleeding = Maroon-coloured blood mixed with stool
less/more frequent o Left colonic bleeding (UC) = Fresh blood mixed
toilets or change in o Anal fissure, Haemorrhoids = Anorectal Bleeding [NOT mixed in stool – only coated!]
stool” • Anorectal Bleeding [COATING OF BLOOD – not mixed in stool]
Anal fissure,
Haemorrhoids • Straining/post-defaecation anal pain
• Thyrotoxicosis = diarrhoea, heat intolerance, irritable, tremor, amenorrhoea
Endocrine
• Hypothyroidism = constipation, cold intolerance, lethargy, menorrhagia
• Drugs (opiates, Fe, antacids, Abs), chronic infection, overflow constipation
Other • lactose intolerance, dietary & lifestyle changes
• bowel obstruction (not passing flatus)
• GORD, but ALSO oesophagitis or malignancy
Heartburn / Regurgitation Ask about chronicity, frequency and medication
• Assoc: weight loss | severity | orthopnoea | PND | Dysphagia | Malignancy | Resp. infection
• If just solids ® mechanical issue /Obstruction
REFLUX / o Internal: oesophageal carcinoma, eosinophilic esophagitis [intermittent], foreign body
SWALLOWING Dysphagia
o External: Retrosternal goitre, mediastinal tumours, bronchial carcinoma
• If liquids ® motility issue | Or issue with BOTH?
DIFFICULTY (Difficulty swallowing)
o MND ® bulbar or pseudobulbar palsy
o Polymyositis, myasthenia gravis
o Progressive worsening = Achalasia, scleroderma
Odynophagia • infectious oesophagitis (E.g. candida, HSV)
(Painful swallow) • radiation or caustic damage to oesophagus
• Intentional vs unintentional
Personal
• Collateral history from relatives about Mental stress or mood is also helpful
ANOREXIA / • Do you feel hungry? Complete loss of appetite? (neurological – hypothalamus)
Early Satiety
WEIGHT LOSS [post-prandial fullness]
• indicator of gastric outlet obstruction or impaired gastric emptying (motility related ® impaired
peristalsis due to diabetes) causing anorexia and weight loss
“Could be caused by:
• What size of pants did you wear 6 months ago? How about now?
GI, systemic, Rapid unexplained
• Have you been on any diet?
psychiatric illness OR weight loss
• Rapid unexplained weight loss is concerning, especially if no recent dietary change
organic disorder”
Weight loss + increased • Malabsorption of nutrients or hypermetabolic state (e.g. thyrotoxicosis)
appetite • Liver disease =taste disturbance (can cause smokers to give up smoking)
Jaundice • Excess bilirubin deposited in conjunctivae and skin® LIVER FAILURE
(see under natural • Have you noticed your skin or eye colour change?
light) •
JAUNDICE / Have you noticed your urine or stool colour change?
• Have you noticed your urine becoming dark or “tea” coloured?
DARK URINE / Dark urine o NOTE: concentrated urine may be called dark urine
STOOL • Pale stool + dark urine = obstructive or cholestatic jaundice (urobilinogen cannot reach intestine)
• Fatty stool = steatorrhea (nutrient malabsorption ® e.g. coeliac disease, pancreatitis
Stool
• Pale stool = post-hepatic jaundice
Pruritis • Itching of the skin (generalised or localised) ® Cholestatic Liver Disease
Lethargy • Tiredness | easy fatigability = acute or chronic liver disease OR anaemia due to GI or chronic IBS
, GIT examination RED FLAG (ACUTE ABDOMEN)
1. REBOUND TENDERNESS
Ask patient to lie 45o (both hands on side) 2. GUARDING/RIGIDITY
3. SEPTIC SIGNS
1. Equipment (e.g. O2, nasogastric feeds, medications?), Vomit bowls, IV infusions, catheters
4. ABSENT BOWEL SOUNDS
2. Jaundice (liver disease)
General 3. Body habitus (obese, cachexia, ascites) “bleed/perforation, obstruction,
inspection 4. Well/unwell (responsiveness) ® Mental state (encephalopathy) / Pain / Agitation (thyrotoxicosis) infarction”
5. Pigmentation (haemochromatosis, Whipple’s disease) & Xanthomata (chronic cholestasis)
• Clubbing (cirrhosis, IBD, coeliac)
• Leuconychia (transverse white lines ® hypoalbumineamia from
chronic liver disease)
Nails • Koilonychia (spoon-shaped nails from severe
Fe or B12/Folate deficiency)
• Terry’s nail (red line on tip of nail) = Chronic liver disease
• Pale palmar creases (anaemia)
• Palmar erythema (chronic liver disease / pregnancy)
• Dupuytren’s contractures (alcohol) = thickened palmar
fascia è fixed finger flexion usually ring or 5th finger
Palms o EtOH, CLD, anti-epileptic
• Asterixis/hepatic flap (hepatic encephalopathy /
uraeamia ® jerky movements of wrist due to toxic
ammonia retention)
• Fingertip capillary glucose monitoring marks (diabetes)
• Measure BP (ask for BP in exam, don’t to do it)
• IV Track marks (® hepatitis C infection?) or tattoos (unregulated pallor, prison)
• Bruising (clotting factor deficiency – Vit K deficiency)
• Spider naevi (chronic liver disease) (> 2 is abnormal) = Blanches
Arms o *Petechiae does NOT blanch
• Muscle Atrophy
• Scratch marks (severe itch (pruritus) = obstructive or cholestatic jaundice = due
to primary biliary cirrhosis and progressive bile duct destruction
• lymphadenopathy
• Acanthosis nigricans = darkening and thickening of skin
Axilla (rarely assoc. with GIT carcinoma)
o Hyperinsulinemia è Acromegaly, PCOS, T2DM
• Uveitis = IBD, autoimmune
• Sclerae: jaundice, anaemia, iritis
• Xanthelasma (biliary cholangitis/cholestasis ® yellowish lipid plaque
in periorbital region)
• Conjunctival pallor (anaemia)
• SLIT-LAMP = Cornea: brown-greenish Kayser–Fleischer rings (Wilson’s
Face /eyes disease) ® (abnormal Cu deposition)® low serum ceruloplasmin & Cu
• Parotidomegaly = XS EtOH, MUMPS, Sjogrens, IgG4 disease
STIGMA OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE:
Ø Jaundice ® hepatic encephalopathy (asterixis)
Ø Hair loss
Ø XS E2 = palmar erythema, spider naevi
Ø Ascites ® SBP
Ø Esophageal varices, caput medusae, haemorrhoids (variceal bleed)
o Angular stomatitis (cracks at corner of mouth) ® Fe, folate or B12
deficiency and water soluble Vit deficiencies (e.g. B2, B6, B12,
B1/thiamine)
o Apthous ulcers (IBD or coeliac disease) = tiny ulcers in lips and mouths
Mouth o Sweet Breath Smell: fetor hepaticus (end-stage chronic liver disease)
• Teeth: Poor dentition (chronic liver disease, alcoholic)
• Gums: gingivitis (smoking), hypertrophy (pregnancy, scurvy),
• Tongue: atrophic glossitis = (Fe, folate or B12 deficiency)
• Cervical lymphadenopathy
• esp. Virchow’s node [eft supraclavicular LN which is linked to GI malignancy]
• Troisier’s signs = presence of Virchow’s node + gastric cancer
• Hyperpigmentation
• heavy metals
• heamochromatosis
• Addison’s
Inspect front/back
Neck/ • Spider naevi [Blanching test = sign of cirrhosis]
Chest • Gynaecomastia (male breast enlargement and body hair loss)
• Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis
• Alcohol = ↓Leydig cell = teste atrophy + gynacomastia
• Drugs (DISCO MTV – digoxin, isoniazid, spironolactone, cimetidine, E2,
methyldopa, TCA, verapamil)
• Endocrine (Hypogonadism, Hyperthyroidism)
• Seminoma (testeicular cancer) = ↑B-HCG, ↑E2
• Cullen’s (central umbilical) and grey-turner’s (flank – retroperitoneal haemorrhage) sign (pancreatitis)
Ask patient to lie flat (both hands on side) + pillow under head FOR ABDO EXAM