BTEC Sports Studies
BONES & THE SKELETAL SYSTEM/FUNCTIONS
LESSON ONE
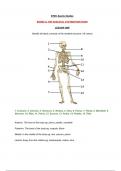
Identify all labels correctly of the skeletal structure (15 marks)
1. Cranium, 2. Clavicle, 3. Humerus, 4. Radius, 5. Ulna, 6. Femur, 7. Fibula, 8. Mandible, 9.
Sternum, 10. Ribs, 11. Pelvis, 12. Sacrum, 13. Pubis, 14. Patella, 15. Tibia
Anterior: The front of the body eg. pelvis, patella, mandible
Posterior: The back of the body eg. scapula, fibula
Medial: In the middle of the body eg. ribs, sacrum, pelvis
Lateral: Away from the midline eg. metacarpals, radius, ulna
,Proximal: Towards the top of the body eg. cranium, mandible, clavicle
Distal: Towards the bottom of the body eg. phalanges, carpals, tibia
Superior: Top eg. Cranium
Inferior: Inferior eg. phalanges
Examples:
-The cranium is superior to the pelvis. This is as the cranium is higher up in the body than the
pelvis.
-The scapula is posterior to the sternum. This is as the scapula is at the back, whereas the
sternum is not
-The humerus is proximal to the ulna. This is as the humerus is higher up in the body than the
ulna.
-The ribs are medial to the humerus. This is as the ribs are closer to the midline than the
humerus is.
Identify the positioning of the skeletal structures (8 marks)
1. The sternum is _______ to the phalanges.
2. The metatarsals are _______ to the cranium.
3. The ulna is _______ from the ribs.
4. The cranium is more _______ than the carpals.
5. The clavicle is more _______ to the tibia.
6. The femur is more ________ than the fibula.
7. The phalanges are more _______ than the vertebrate.
8. The scapula is _______ to the humerus.
1. Medial, 2. Inferior, 3. Lateral, 4. Anterior, 5. Superior, 6. Proximal, 7. Distal, 8. posterior
LESSON TWO:
Types Of Bone:
Long Bones: Found in the arms and legs and are longer than wide. They are involved in
movement and blood cell reproduction. Eg. femur, humerus, radius, tibia, phalanges,
metacarpals, metatarsals
Short Bones: Cube like in appearance. Found in ankles, feet, wrists, and fingers. Help with
stability and weight bearing. Eg. carpals, tarsals.
Flat Bones: Strong, flat plates. Provided for protection of organs and attachment for muscles.
Eg. scapula, cranium, ribs, sternum, pelvis
, Irregular Bones: Irregular and unusual in shape. Used for protection and movement eg.
vertebrae
Sesamoid Bones: Short/irregular bones usually found with a tendon. They have a smooth
surface and reduce friction. Eg. patella
Functions Of Skeleton:
Sports Support
People Protection
Are Attachment to muscles
Best Blood cell production
Winning Weight bearing
Long Leverage
Race Reduction friction
Miles Minerals
Support: Bones providing framework for the body.
Protection: Bones (particular flat bones) protect delicate areas of the body for organs eg. The
skull protects the cranium.
Attachment to muscles: Muscles are attached to our skeleton by tendons. As they contract, they
pull (flat) bones causing them to move.
Blood production: Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow (long bones).
Weight bearing: Bones are strong to support the weight of our body/tissues. The strength of our
bones can help prevent injury.
Leverage: When muscles pull on bones (long bones), they act as levers to produce movement
Reduction friction: synovial joints secrete synovial fluid to lubricate the joints to prevent the
bones (sesamoid) from rubbing together, reducing friction.
Mineral storage: Minerals eg. calcium and phosphorus are stored in bones which are essential
to bone growth and health
QUESTIONS:
1. What is the bone in the femur classified as? (1 mark)
2. Give two advantages of a short bone (2marks)