FWeb Systems (COM1025)
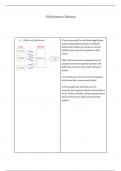
1) What is a Client Server? Client-server model is a distributed application
structure that partitions tasks or workloads
between the providers of a resource or service,
called servers, and service requesters, called
clients.
Often clients and servers communicate over a
computer network on separate hardware, but
both client and server may reside in the same
system.
A server host runs one or more server programs,
which share their resources with clients.
A client usually does not share any of its
resources, but it requests content or service from a
server. Clients, therefore, initiate communication
sessions with servers, which await incoming
requests.
,2) How do web pages work? The browser sends an HTTP request message to
the server, asking it to send a copy of the website
to the client. This message, and all other data sent
between the client and the server, is sent across
an internet connection using TCP/IP.
▪ Hypertext documents are more
commonly known as web pages.
▪ Hypertext documents may link to
hypermedia documents, i.e., non-
hypertext documents (e.g. an
image, a video, a textual file
without any special structure).
▪ A web page or a hypermedia
document normally resides on a
remote computer (called a web
server) over the Internet so they
can be accessed by people from
anywhere in the world.
✓ Each web page or hypermedia
document has a web address, or
more formally a URL (Uniform
Resource Locator) which mainly
tells where it is.
▪ Web pages are written in a
markup language called HTML.
▪ Browsers display a web page by
reading and interpreting its HTML.
3) What is a URL? ▪ A Uniform Resource Identifier
(URI) is a string of characters used
to identify a resource
▪ The most common form of URI is
the Uniform Resource Locator
(URL), frequently referred to
informally as a web address, e.g.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/
✓ Web browsers request pages
from web servers by using a URL
▪ Some URIs refer to a location
within a resource.
✓ This kind of URI ends with "#"
followed by an anchor identifier
(called the fragment identifier) – see next.
,4) What is the difference between a Relative An absolute URL contains all the information
and Absolute URL? necessary to locate a resource.
A relative URL locates a resource using an
absolute URL as a starting point. In effect, the
"complete URL" of the target is specified by
concatenating the absolute and relative URLs.
An absolute URL uses the following format:
scheme://server/path/resource
A relative URL typically consists only of the path,
and optionally, the resource, but no scheme or
server. The following tables define the individual
parts of the complete URL format.
Scheme = Specifies how the resource is to be
accessed.
Server = Specifies the name of the computer
where the resource is located.
Path =Specifies the sequence of directories
leading to the target. If resource is omitted, the
target is the last directory in path.
Resource = If included, resource is the target, and
is typically the name of a file. It may be a simple
file, containing a single binary stream of bytes, or
a structured document, containing one or more
storages and binary streams of bytes.
5) What are the different types of schemes? ❖ http: documents retrieved via a
protocol called HTTP.
❖ https: documents retrieved via a
protocol called HTTPS.
❖ file: documents accessible from
the local machine.
❖ ftp: documents retrieved via a
protocol called FTP.
, ❖ mailto: documents to be sent to the given
email address (emails)
6) What are the different types of URL Full syntax:
syntaxes? ✓
scheme:[//[[userinfo@]host[:port]]]
[path][?query][#fragment]
Two slashes (//): When the authority component
is absent, the path
component cannot begin with two slashes.
Authority:
✓ A naming authority for parsing
parts of the URL.
✓ userinfo (optional)
✓ host (mandatory)
❖ Domain name (or IP address) of
the web site (server).
❖ An optional authentication
section of a user name and
password, separated
by a colon, followed by @
❖ The passing of authentication
information in clear text has
proven to be
a security risk in almost every case where it has
been used.
Port (optional):
❖ Port number used by the
scheme (protocol).
• In programming, it may specify a particular
server program on a computer in a network.
Path:
✓ Location of the document on the
hosting machine (using “/” as the
path separator).
Query String:
✓ A list of data sent to the web
server, in the format
“name_1=value_1&…&name_n=value_n”.
✓ Typical URL containing a query