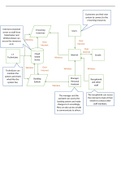
• Evolution occurs when heritable characteristics of a species change.
• The fossil record provides evidence for evolution by revealing the features of an ancestor for
comparison against living descendants.
• Selective breeding of domesticated animals such as cows and dogs shows that artificial
selection can cause evolution.
• Comparing the anatomy of different organisms can be used to determine a common ancestor:
• Homologous structures are structurally similar but used for different things.
• Analogous structures have different origins/ancestors
but perform the same function.
• Homologous structures illustrate adaptive radiation
which is where organisms diversify rapidly from their
ancestors due to changes in the environment, e.g
pentadactyl limb ⟶
• Genetic variation within a species is described as
continuous and fits a normal distribution curve.
• If two populations of a species are exposed to different
environmental factors, their genetic compatibility will decrease as they evolve causing the
populations to diverge into different species, a process known as speciation.
• An example of this is peppered moths, which are usually white and camouflage on birch trees.
After the industrial revolution the mutated darker moth had a selective advantage as the trees
were covered in soot, causing numbers to grow.
Unit 5.2
• Natural selection: Genetic variation exists in a population causing competition. Those best
adapted to survive are more likely to reproduce and pass on their genes, resulting in a change in
allele frequency within the population over generations (more of one variation).
• Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction causes variation in a species (see Unit 10).
• Species tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support, leading to
competition for survival known as survival of the fittest.
• Adaptations make an individual more suited to its environment. They are passed to offspring.
• An example of adaptive radiation and natural selection are the beak types seen in the finches on
Daphne Major.
• In 1977 a drought occurred resulting in plants producing seeds with harder casings. Because of
this, the average beak size increased as those with bigger beaks were able to crack and eat
more seeds.
• An example of survival of the fittest is antibiotic resistance. When treated with antibiotics, the
antibiotic resistant bacteria will remain whilst other bacteria is killed, allowing the antibiotic
resistant bacteria to reproduce, causing the gene to become more frequent.
Unit 5.3
• Taxonomic rank: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family genus species (“Kinky People Can Often
Find Good Sex”).
• The Binomial name is used to classify species using the genus and species e.g Homo sapien.
• The three domains of life are archaea, bacteria and eukarya.