Josh Lavery
Anatomy and Physiology, Unit 1, Task 1
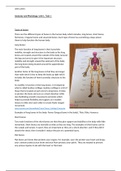
Types of bones
There are five different types of bones in the human body which includes, long bones, short bones,
flat bones, irregular bones and sesamoid bones. Each type of bone has something unique about
them to help function the human body.
Long bones:
The main function of long bones is that it provides
mobility, strength and structure to the body as the long
bones are located around the outside of the body (around
the legs and arms) to give it the important structure,
mobility and strength around the axial part of the body,
the long bones being located around the appendicular
part of the body.
Another factor of the long bones is that they are longer
than wide which is key to keep the body up right which
includes the function of how it provides structure to the
body.
As mobility is function of the long bones, it is helped by
what is called hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is a bit of
tissue that is located at each end of a long bone, it helps
to protect the bone and acts as a shock absorber while
also facilitating smooth movements and joints which
helps to provide flexibility and support as it enables
tissues to slide over each other to create freely ranged
movement.
www.ivyroses.com/HumanBody/Tissue/Tissue_Cartilage-Tissue.php
Examples of long bones in the body: Femur (longest bone in the body), Tibia, Fibia, Humerus
Short bones:
Two main functions of the short bones are that they give support and stability to the body with little
movement. Short bones are normally as wide as they are long. The examples of short bones can be
the carpals and tarsals. In sport, they are important as they are a shock absorber, and if they didn’t
absorb the shock, then it wouldn’t reduce the pain of a potential injury.
Flat bones:
Flat bones are bones that protects your organs. For example, your ribs protect your heart and lungs,
your cranium protects your brain and your ilium protects your pelvis. They are needed to prevent
any serious injuries to do with the heart or the brain.
, Josh Lavery
Irregular bones:
The function of irregular bones is that they provide protection of nervous tissue and muscle
attachment. An example of the irregular bones is the vertebrae column the vertebrae column is in
the spine and has 5 different types in the column that consist of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar,
sacrum and coccyx. The vertebrae column is formed from 33 separate bones. 7 in the cervical, 12 in
the thoracic, 5 in the lumbar, 5 in the sacrum and 4 in the coccyx.
Sesamoid bones:
Sesamoid bones are bones that are located around joints and provide movement typically found in
the hands and feet where the metacarpals, carpals, etc are located. Another example of the
sesamoid bone can also be found in the knee (patella). These bones are small more or less rounded
masses embedded in certain tendons and usually related to joint surfaces.
The two types of skeleton:
There are two types of skeleton in the body, the axial and appendicular.
Axial: The axial skeleton is in the centre of the body and its main function is to provide support and
protection to the brain and to the heart and other vital body organs. It also provides sites for the
attachment of other bones and muscles in the body and protects the nerves and blood vessels from
the brain and spinal cord. In the axial skeleton it consists of bones such as the cranium, ribs, ilium as
well as the vertebral column which is also needed for support and protection as it is a vital body
part.
Appendicular: The appendicular is found around the arms, legs and hip. The function of the
appendicular skeleton is mainly movement as well as holding and supporting the limbs which allow
humans to walk and grasp/manipulate objects. The bones that are found in the appendicular
skeleton are: Femur, Tibia, Ulna, Radius, Fibia, Humerus, etc.
Functions of the skeletal system:
There are five types of functions of the skeletal system. These include: Protection, Attachment of
muscles, store of minerals, Support and red and white blood cell production.
Protection:
Protection is where the bones provide a framework for muscles to attach. Then when the muscles
contract they pull on the bones of the skeleton, which act like levers to create movement. Your
muscles and organs can connect to things where ribs protect the heart and lungs, and your cranium
protecting your brains, this topic links to the flat bones as flat bones are bones that help protect
your organs, examples being cranium and ribs.
Attachment for skeletal muscle:
Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibres. Collagen is a type of
protein fibre found abundantly throughout our body. It provides strength and cushioning to many
different areas of the body, including the skin. More specifically, collagen is found in our various
types of connective tissues such as cartilage, tendons, bones, and ligaments.