CHAPTER 4 :
THE macro economy
4. 1 WHAT IS THE MACRO ECONOMY ?
the whole
1¥ →
economy as a
0 level of economic activity determined by aggregate demand (Ab)
and aggregate supply ( AS ) .
4. 2 GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT ( GDP)
= UNDERSTANDING GDP =
o measures total income of everyone in the economy
o measures total expenditure on economy 's output of Gbs .
<
Producer 's consumer buy Gbs
income = expenditure
profits 7
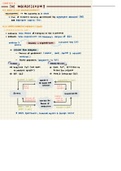
→ circular flow diagram :
-
factors of production ( labour ,
land , capital & natural
resources )
factor payments ( payments to FOP )
FIRMS HOUSEHOLDS
⇒ buy / hire Fop ( use them ⇒ own FOP ,
sell / rent to
to produce goods ) firms for income
⇒ sell G&S ⇒ buy & consume Gbs
revenue ( = GDP ) markets spending ( = Gop ,
<
for goods and
>
services Gas
Gbs
sold bought
✓ ~
firms households
labour '
n factors of land & ^
production market for capital
<
factors of
>
wages rent & Production
,
income f- GDP )
profit ( = GDP )
* omits government , financial system a foreign sector
,= DEFINITION OF GDP =
↳ market value of all final goods & services produced within
a country in a
given time .
① market value
-
value of GIs @ selling price 1 same units e. g. us b)
-
✗ market value e. g. household chores EXCLUDED
② final Gbs
-
intended for consumer usage
-
intermediate goods : components / ingredients
{
embodies
baking . . .
value of
> intermediate
goods
$10.00 $15.00
③ within a country
-
production which occurs within a country 's borders
I can be done by citizens / foreign workers )
④ given period of time
-
currently produced goods ( not in the past )
- v 3- 12 months > house I built 2018 ) bought in 2021
,
:> ✗ counted in 2021 GDP
= components OF GDP =
① consumption ( C )
-
total spending by households on Gbs
↳ housing costs
t >
landlords ( imputed rental value ONLY )
tenants
①
trent payment )
✗ purchase price / mortgage payments
② investment III
-
total spending on goods that will be used to produce other goods in
the future
↳ capital equipment ( machinery ) ,
infrastructure ,
inventories
( produced but not sold yet ]
,③ government spending (G)
-
total spending on Gbs purchased by government
↳ transfer payments e. g. unemployment insurance benefits ,
pensions
↳ public goods & merit goods
④ net exports ( NX )
-
total foreign spending on economy 's GIs [ exports ]
-
portion of C , I & G spent on G&S produced abroad [ imports ]
MX =
exports -
imports
: .
GDP calculation : GDP = C + I t G + NX
=
WHAT IS GDP USED FOR ? =
o real GDP per capita → main indicator of average person 's standard
of living
BUT ! ! does not value : childcare etc
_
,
-
quality of environment -
non -
market activity
-
leisure time -
equitable income distribution
o
large GDP allows countries to afford :
L cases where people may be
-
better schools poorer / richer than depicted
-
cleaner environment
-
quality healthcare
* Hbl positively correlated WI GDP
specific to each Gbs ( Mb )
4. 3 AGGREGATE DEMAND ( Ab )
aggregate demands > total spending on an economy 's Gas @ given
N v r - revert
price level in a given time period
price level
.
n > shows quantity of GIS that households ,
firms & governments want to buy @ each
nationwide basis ; level
price
all Gds
o
negative relationship 1 inverse ) with
A
price level : . downward sloping
AD
0
Consists of 4 components
0 >
real GDP
, =
WHY IS AD DOWNWARD SLOPING ? =
① wealth effect 1 price level
G consumption )
price level tr ; real value of money 4 .
I higher spending power )
"
wealthier spend more
"
i. consumers are =
↳ consumer spending 4 ; demand for GIS 4 .
}
$5 $20 Purchasing
⇒ power
T
4 cones 10 cones
$2 : feels richer
/ THEN , ( now , .
,
ADR
② interest rate effect ( price level & investment )
price level W ; interest rate to
less borrow
expensive to
i. spending on investment goods 4 from banks
;
G&S demanded 4
low price usually due to deflation 1 bad economy )
gov discourage money in banks
•
keeping
: .
interest rate tr
??? INVESTMENT > more worth it
③ exchange rate / international effect 1 price level & net exports )
price level to ; interest rates to ; real exchange rate
HOWEVER ,
net exports 1^1 export price 4 : . more countries
i. Ab R purchase ( exports > imports )
summary ⇒ price level tr ,
Ab tr .
= components OF AGGREGATE Demand =
C-
consumption
}
↳ consumer confidence 9 income tax tr ,
,
wealth R money supply 9 , population A
,
G government spending
-
↳ desire to stimulate economic activity I
win political support 4 curve
I -
investment shifts
right
↳ business confidence 4 , corporate tax T ,
technological advances .
NX -
net exports
↳ man , ,, , , .mn, , , .mg, , .mu, ,
incomes in foreign countries 4 .