Psychopathology
Definitions of abnormality
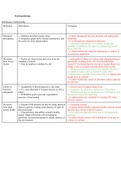
Definition Description Evaluation
Statistical → Statistics describe typical values → Cannot distinguish between desirable and undesirable
Infrequency → frequency graph shows normal distribution, and behaviour
the ends of it show abnormalities → Cut off point for abnormal is subjective
→ Sometimes appropriate, for example, intellectual
disability is defined as less than two standard deviations
below mean IQ
→ Cultural relativism: statistical infrequency is relative to
the reference population
Deviation → Norms are what society perceives to be the → Susceptible to abuse as it varies with changing attitudes
from Social standard of normal and morals, isolating those who are nonconformists;
Norms → May be implicit or defined by law Szasz(1974) claimed that the concept of mental illness was
simply a way to exclude nonconformists from society
→ Related to context and degree, for example, shouting is
acceptable in some contexts and not in some other
→ distinguishes desirable from undesirable but implies that
people have to conform
→ Cultural relativism: norms of dominant culture imposed
on minority
Failure to → incapability of performing day to day tasks → Distress may be judged subjectively
Function → It is only abnormal if it causes distress to self or → recognizes the subjective experience of the patient
Adequately others → The behaviour may be functional, as it will lead to extra
→ WHODAS used to provide a quantitative attention for those who need help
measure of functioning → Cultural relativism: standards of everyday life varies
between cultures
Deviation → Jahoda(1958) pointed out that we define physical → Unrealistic criteria
from ideal illness in part by looking at the absence of signs of → Equates mental health to physical health, whereas mental
mental health physical health illnesses may not have physical causes
→ Characteristics that define mentally healthy → It is a positive approach that is part of the humanistic
people: High self esteem, self actualisation, approach
autonomy, accurate perception of reality, mastery of → Cultural bound criteria: self actualisation is not part of
the environment collectivist cultures
, Mental Disorders
emotional;cognitive;behavioural
Mental Disorder Description
OCD anxiety and distress, and awareness that this is
excessive, leading to shame
recurrent, intrusive, uncontrollable thoughts, more
than everyday worries
compulsive behaviours to reduce obsessive
thoughts, not connected in a realistic way
Phobias excessive fear, anxiety and or panic cued by a
specific object or situation
not helped by rational argument, unreasonableness
of the behaviour recognized
avoidance, faint or freeze, interferes with
everyday life
Depression negative emotions such as sadness, loss of interest
and sometimes anger
irrational, negative thoughts and self beliefs that
are self fulfilling
reduced or increased activity related to energy
levels, sleep and or eating