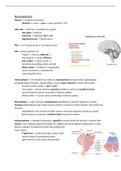
Neuroanatomy
Neuron → Synaptic transmission
Dendrite → soma → axon → axon terminal → NTs
Glial cells → Structure, metabolism & support
Microglial → Defence
Astrocyte → Nutrition, BBB & NGF
Oligodendrocyte → Myelin axons
PNS → 12 P cranial nerves & 31 P spinal nerves
CNS → Brain & spinal cord
Triptych → Sensory (afferent) →
interneurons → motor (efferent)
Grey matter → cortex/ nuclei →
centrally surrounding canalis centralis
White matter → initiation & organisation
motor movements → peripherally
containing fibre tracts
Telencephalon → 2 hemispheres (cerebrum), hippocampus (temporal lobe), basal ganglia,
amygdala, lateral ventricle, choroid plexus, insula, corpus callosum (connect left & right)
Increase cortical surface → gyri & sulci
Grey matter → dorsal striatum (putamen, lentiform nucleus & caudate nucleus),
ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens) & globus pallidus
White matter → Corona radiata continuing in internal capsule
Diencephalon → optic cup (eye), hypothalamus (behaviour & visceral/ autonomic control),
thalamus (bidirectional relay centre cortex), anterior commissure, third ventricle, interventricular
foramen
Hypothalamus also involved in limbic system, hormonal regulation (pituitary), pineal
gland produces melatonin, mamillary body (memory formation)
Mesencephalon → belongs to brainstem, aqueduct (connect 3rd & 4th ventricle, contains CSF),
tectum (roof, colliculus superior & inferior for auditive and visual reflexes), tegmentum, cranial
flexure (cephalic) & pedunculi cerebri (descending fibre
tracts motor)
Tegmentum → substantia nigra, nucleus ruber
(motor control), periaqueductal gray
(pain control) & red nucleus (locomotion)
, Rhombencephalon → fourth ventricle (between metencephalon & myelencephalon)
Metencephalon → cerebellum (compare info from SPC and how it’s planned, can
correct) & pons (bridge cerebellum & cortex, nuclei of cranial nerve V)
Motor system → crossing fibres from and to cerebellum
Inferior cerebellar peduncle → connects cerebellum to medulla
Middle cerebellar peduncle → connects cerebellum to pons
Superior cerebellar peduncle → connects cerebellum to mesencephalon
Myelencephalon → medulla, cranial nerves VI-XII, sensory, motor & visceral nuclei
Spinal cord → central canal
Meninges (membranes) → Dura mater (tough), Arachnoid (spidery) & Pia mater (soft)
Superior cerebral veins beneath arachnoid
Central sulcus → border frontal lobe & parietal lobe (lateral)
Lateral sulcus → border temporal lobe & frontal lobe
Parieto-occipital sulcus → border parietal lobe & occipital lobe
(lateral)
Hypothalamic sulcus → border thalamus & hypothalamus
Sulcus limitans → border between basal lamina & alar lamina
Sensory neurons in dorsal & motor in ventral
Primary visual cortex → occipital lobe
Primary auditory cortex → temporal lobe
Wernicke’s aphasia = lesion next to left auditory cortex
(weird sentences)
Motor cortex → frontal lobe
Sensory cortex → parietal lobe
Prefrontal cortex → frontal lobe
Broca’s aphasia = lesion to left frontal cortex (can’t say what u want)
Motor cortex thicker than sensory due to pyramidal neurons
Layer I → molecular
Layer II & III → cross integration small pyramidal
cell
Layer IV → afferent fibres from thalamus
Layer V → large pyramidal cells (motor
projection to brainstem & Sp cord)
Layer VI → projections to thalamus
(corticothalamic, pyramidal tract,
thalamocortical, short association &
cholinergic/aminergic)