Maren Stijnen
S2855992
Stem cells in drug research – Assignment 1
Compound Hazards Precautions
Isoproterenol Harmful if swallowed. Avoid breathing dust, fumes, etcetera.
Causes skin and eye irritation. Wear protection, gloves, glasses, clothing.
May cause respiratory irritation. 1 Rinse thoroughly after contact and wash hands after handling. 1
Ryanodine Harmful if swallowed. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Very toxic to aquatic life, with long Avoid release to the environment.
lasting effects.2 If swallowed, rinse mouth and call poison center or doctor if you
feel unwell.2
Nifedipine Harmful if swallowed. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Suspected of damaging fertility or the Wear protective gloves, clothing, glasses.
unborn child.3 Immediately call a doctor after swallowing. 3
Verapamil Toxic if swallowed. Avoid breathing dust, fumes, etcetera.
Toxic in contact with skin. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Fatal if inhaled.4 Wear protective gloves and clothing
Immediately call poison center/doctor if swallowed. 4
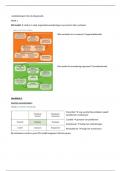
b) Isoproterenol is an agonist for beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptors. Beta-1 receptors are located in heart tissues,
while beta-2 receptors are located on smooth muscles.5 Once isoproterenol binds to the receptor, through
different second messengers, protein kinase A (PKA) is activated. The activated PKA phosphorylates L-type
calcium channels present in cardiomyocytes. The phosphorylation results in an increase in intracellular calcium.
In cardiac pacemaker cells, this increase in calcium will result in a steeper slope of phase 4 of the cardiac
pacemaker action potential, which causes the cells to reach the threshold quicker, and thus in an increased heart
rate. In non pacemaker myocytes, the increased calcium will result in an increased contractility.6
Ryanodine is a plant alkaloid which binds to ryanodine receptors (RyRs). 7 RyRs are intracellular calcium channel
proteins, found in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of skeletal and cardiac muscles.8 At low concentrations
ryanodine, the channel is long term opened, which results in a high outflow of calcium , allowing muscles to
contract. At high concentrations, the calcium channels are blocked, and calcium can no longer pass through.7,8 In
cardiac muscles, administration of ryanodine results in a reduction of contractility due to the reduced calcium
release.9,10
Nifedipine blocks voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels present in cardiomyocytes. Under normal
circumstances, calcium ions use these channels to move into muscle cells during depolarization. Because of the
obstruction, calcium can no longer travel into the cells. Reduction of intracellular calcium reduces activity of the
cells and the peripheral arterial vascular resistance, therefore lowering the blood pressure and increasing the
delivery of oxygen to the myocardium.11–13 No significant effect of nifedipine is found on the heart rate. 14
Verapamil blocks L-type calcium channels by binding to the alpha-1 subunit which is highly expressed. Calcium
influx results in contraction of muscle tissue and activity in the hearts pacemaker. Verapamil binds dependent
on voltage and frequency. This means that the affinity increases once the membrane potential is reduced and
with an excessive depolarizing stimulus. By inhibition of the channel and calcium influx, muscle contraction is
prevented. Also, the decrease of influx increases the refractory period of the AV node and slows conduction, this
means the heart rate is slowed down.15
c) Both verapamil and ryanodine result in a decrease in the heart rate. They both do this via different
mechanisms. Verapamil blocks the influx of extracellular calcium by blocking L-type calcium channels
on the membrane, ryanodine blocks intracellular calcium channels on the SR. The blocking of RyRs
results in high concentrations of intracellular calcium. This will not be the case in verapamil as this
blocks the initial influx of calcium. By measuring the intracellular calcium, a difference could be seen
in ryanodine and verapamil therapy, where a higher level would be expected after ryanodine therapy.
d) Bradycardia is defined as a slow, irregular heart rate. Isoproterenol indirectly phosphorylates
calcium channels, which increases intracellular calcium. This eventually results in an increased heart
rate, which is exactly what is needed in patients with bradycardia. Therefore, isoproterenol would be
useful in the treatment of bradycardia.
S2855992
Stem cells in drug research – Assignment 1
Compound Hazards Precautions
Isoproterenol Harmful if swallowed. Avoid breathing dust, fumes, etcetera.
Causes skin and eye irritation. Wear protection, gloves, glasses, clothing.
May cause respiratory irritation. 1 Rinse thoroughly after contact and wash hands after handling. 1
Ryanodine Harmful if swallowed. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Very toxic to aquatic life, with long Avoid release to the environment.
lasting effects.2 If swallowed, rinse mouth and call poison center or doctor if you
feel unwell.2
Nifedipine Harmful if swallowed. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Suspected of damaging fertility or the Wear protective gloves, clothing, glasses.
unborn child.3 Immediately call a doctor after swallowing. 3
Verapamil Toxic if swallowed. Avoid breathing dust, fumes, etcetera.
Toxic in contact with skin. Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Fatal if inhaled.4 Wear protective gloves and clothing
Immediately call poison center/doctor if swallowed. 4
b) Isoproterenol is an agonist for beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptors. Beta-1 receptors are located in heart tissues,
while beta-2 receptors are located on smooth muscles.5 Once isoproterenol binds to the receptor, through
different second messengers, protein kinase A (PKA) is activated. The activated PKA phosphorylates L-type
calcium channels present in cardiomyocytes. The phosphorylation results in an increase in intracellular calcium.
In cardiac pacemaker cells, this increase in calcium will result in a steeper slope of phase 4 of the cardiac
pacemaker action potential, which causes the cells to reach the threshold quicker, and thus in an increased heart
rate. In non pacemaker myocytes, the increased calcium will result in an increased contractility.6
Ryanodine is a plant alkaloid which binds to ryanodine receptors (RyRs). 7 RyRs are intracellular calcium channel
proteins, found in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of skeletal and cardiac muscles.8 At low concentrations
ryanodine, the channel is long term opened, which results in a high outflow of calcium , allowing muscles to
contract. At high concentrations, the calcium channels are blocked, and calcium can no longer pass through.7,8 In
cardiac muscles, administration of ryanodine results in a reduction of contractility due to the reduced calcium
release.9,10
Nifedipine blocks voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels present in cardiomyocytes. Under normal
circumstances, calcium ions use these channels to move into muscle cells during depolarization. Because of the
obstruction, calcium can no longer travel into the cells. Reduction of intracellular calcium reduces activity of the
cells and the peripheral arterial vascular resistance, therefore lowering the blood pressure and increasing the
delivery of oxygen to the myocardium.11–13 No significant effect of nifedipine is found on the heart rate. 14
Verapamil blocks L-type calcium channels by binding to the alpha-1 subunit which is highly expressed. Calcium
influx results in contraction of muscle tissue and activity in the hearts pacemaker. Verapamil binds dependent
on voltage and frequency. This means that the affinity increases once the membrane potential is reduced and
with an excessive depolarizing stimulus. By inhibition of the channel and calcium influx, muscle contraction is
prevented. Also, the decrease of influx increases the refractory period of the AV node and slows conduction, this
means the heart rate is slowed down.15
c) Both verapamil and ryanodine result in a decrease in the heart rate. They both do this via different
mechanisms. Verapamil blocks the influx of extracellular calcium by blocking L-type calcium channels
on the membrane, ryanodine blocks intracellular calcium channels on the SR. The blocking of RyRs
results in high concentrations of intracellular calcium. This will not be the case in verapamil as this
blocks the initial influx of calcium. By measuring the intracellular calcium, a difference could be seen
in ryanodine and verapamil therapy, where a higher level would be expected after ryanodine therapy.
d) Bradycardia is defined as a slow, irregular heart rate. Isoproterenol indirectly phosphorylates
calcium channels, which increases intracellular calcium. This eventually results in an increased heart
rate, which is exactly what is needed in patients with bradycardia. Therefore, isoproterenol would be
useful in the treatment of bradycardia.