2019 Q1 Programming Summary
Running a Java program: (1) type the text with at least 1 class (2) save file with name class
(3) compile file (checks for errors) (4) run the class file.
For naming things, use CamelCase(start each new word in a name with an uppercase letter)
Types of rules: (1) syntax (grammar) (2) semantic (meaning) (3) conventions (wise advice)
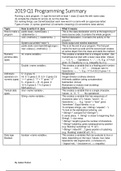
Topic How to write it in Java What it means
How to make a public class <nameClass> { This is the class declaration and is at the beginning of
program <statements> } every source code, it contains the whole program.
void <method>() { <statements> } Method declaration, it contains the activity of the
program.
System.out.println(“<text>”); Gives output and newline statement
public static void main(String[] args) { This is at the end of your program. The first part
new <class>().<method>(); } marks the start-up code and the second part creates
an active object from the class and starts the method.
Numeric/ int <name variable>; This creates a variable that is a integral number. Use
primitive data CamelCase but start with a lower case letter. Values:
types …, -1, 0, 1, … . Operations: +, -, *, /, %. E.g. (17+4)/2
gives 10. Equality by x==y, inequality by x!=y
Double <name variable>; This creates a variable that is a floating point number.
Values: … , -0.5, …, 0.7, … . (in)equal: see int.
Operations: +, -, *, / E.g. (17.0+4.0)/2.0 gives 1.5
Arithmeric 5 * 2 gives 10 Multiplication
operators (on Int: gives 2. D: 5. gives 2.5 Integer division (ordinary division)
numeric types) 1 + 1 gives 2. “1” + “1” gives “11” Arithmetic addition (string concatenation)
5 – 2 gives 3. – (5 - 2) gives -3 Subtraction (minus)
10 % 5 gives 0. 7 % 5 gives 2 Remainder or modulo (rest bij deling)
Math.pow(x,y) Machtsverheffen (x^y)
Textual data char <name variable>; This creates a variable that is a single character.
types Values: ‘a’, ‘0’, ‘?’, … . No operations!
String <name variable>; This creates a variable that has sequences of
characters (also “a”!). Values: “seven”, “a”, …
Operations: +, … E.g. “seven” + ”teen” gives
“seventeen”. Equal identity: x==y.
To compare strings, use “<String>”.equals(“...”).
To look at the alphabetical ordering, use
“<String1>”.compareTo(“<String2>”).
0: same place, -1: String1 is closer to beginning than
String2, 1: vice versa.
“<String>”.length() gives the number of characters.
“<String>”substring: gives subsequence by position
(e.g.“Building”.substring(1,4) → “uil”)
“<String>”.indexOf(“…”):gives position of substring
(e.g. “Building”.indexOf(“uil”) → 1)
Data type boolean <name variable>; This creates a variables that can evaluate to true or
Boolean false, depending on the input. Values: true, false
Operations: && (logical and), || (inclusive or),
! (logical not), ^ (exclusive or), == (equality)
1
By Isabel Rutten
, 2019 Q1 Programming Summary
Comparison 5 +7 == Comparing all primitive types (int, double, Boolean)
operators gives a true or false, it’s a Boolean value.
<string1>.equals(<string2>) Comparing String types (DON’T USE ==)
Scanner Input import java.util.Scanner; The user can insert values which can be used in the
class <name> { program by applying a scanner. Here, you can see all
Double amount; the necessary parts of using a scanner.
This: Scanner = new When no input is available, the scanner waits for
Scanner(System.in); input.
Public void <method>() { “scanner” can also be replaced by another word.
amount = scanner.nextDouble(); } Variants of “scanner.nextDouble()” (which reads the
Or like this: Scanner; next Double & stores it) are “scanner.nextInt()” (for
Public void <method>() { integers), “scanner.next()” (for Strings/a word),
scanner = new Scanner(System.in); “scanner.nextLine()” (for lines (whole line=String)).
amount = scanner.nextDouble; } It is also possible to “read” whether there even is a Int
or a Double with “scanner.hasNext()” (e.g.
scanner.hasNextDouble() checks for Doubles). These
statements will return “true” or “false.
If-construct if ( condition ) { The if-construct is used to execute statements only
... then-part when the condition is true, uses Boolean expressions.
} else { Here you can see the if-else construct.
... else-part If you leave out the part in bold, you have a if-
} construct with one branch only.
if ( A ) { Here you can see the if-else if construct.
... executed if A is true
} else if ( B ) {
... executed if B is true and A is not
true
} else if ( C ) {
... executed if C is true and neither A
nor B are true
} else {
... executed if A nor B nor C is true
}
if ( A1 ) { Here you can see the usage of nesting. This is hard to
if ( B1 ) { manage so it is better not to use it!
... A1 true and B1 true If you do, try to figure out what each branch means:
} else { this way you can avoid errors.
... A1 true and B1 false
}
} else {
if ( B2 ) {
... A1 false and B2 true
} else {
... A1 false and B2 false
}}
2
By Isabel Rutten