Samenvatting
Research Project Final Exam Summary
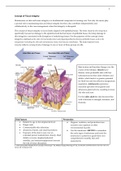
A summary of the contents of the lectures and workshops of block 7 of the Research Projects course
[Meer zien]
Studenten hebben al meer dan 850.000 samenvattingen beoordeeld. Zo weet jij zeker dat je de beste keuze maakt!

Geen gedoe — betaal gewoon eenmalig met iDeal, creditcard of je Stuvia-tegoed en je bent klaar. Geen abonnement nodig.

Studenten maken samenvattingen voor studenten. Dat betekent: actuele inhoud waar jij écht wat aan hebt. Geen overbodige details!
Je krijgt een PDF, die direct beschikbaar is na je aankoop. Het gekochte document is altijd, overal en oneindig toegankelijk via je profiel.
Onze tevredenheidsgarantie zorgt ervoor dat je altijd een studiedocument vindt dat goed bij je past. Je vult een formulier in en onze klantenservice regelt de rest.
Stuvia is een marktplaats, je koop dit document dus niet van ons, maar van verkoper 556933er. Stuvia faciliteert de betaling aan de verkoper.
Nee, je koopt alleen deze samenvatting voor €4,99. Je zit daarna nergens aan vast.
4,6 sterren op Google & Trustpilot (+1000 reviews)
Afgelopen 30 dagen zijn er 65040 samenvattingen verkocht
Opgericht in 2010, al 15 jaar dé plek om samenvattingen te kopen