Overig
Criminality, Cognition and Personality
- Instelling
- Tilburg University (UVT)
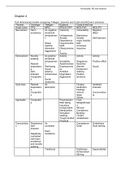
This document categorized the information from the book of Criminality, Cognition and Personality in tables. For example, the various models are explained with what the terms mean
[Meer zien]