Summary
Intercultural Sensitivity
Anika Ochel
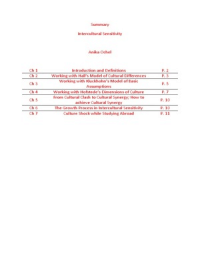
Ch 1 Introduction and Definitions P. 2
Ch 2 Working with Hall’s Model of Cultural Differences P. 3
Working with Kluckhohn’s Model of Basic
Ch 3 P. 5
Assumptions
Ch 4 Working with Hofstede’s Dimensions of Culture P. 7
From Cultural Clash to Cultural Synergy; How to
Ch 5 P. 10
achieve Cultural Synergy
Ch 6 The Growth Process in Intercultural Sensitivity P. 10
Ch 7 Culture Shock while Studying Abroad P. 11
, Cultural Awareness: Introduction and Definitions
What is Culture? Visible and Invisible Culture
Artefacts of Culture (outer layer)
the first thing you notice when entering a new country/company
possible artefacts of a company: logo, house-style, how employees dress
Norms and Values (second layer)
written and unwritten standards of correct, desired behaviour
norms and values are not as visible as artefacts
Basic Assumptions (deepest layer)
abstract and invisible
we learn them very young (before we are 7)
unaware of their influence
Definition of Culture
culture is about the familiar way we think, feel and behave
Geert Hofstede: Culture is the collective programming of the mind, which distinguishes the
members of one group or category of people from another.
Edgar Schein: A pattern of shared basic assumptions that the group learned as it solved its
problems of external adaptation and internal Integration, that has worked well enough to be
considered valid and therefore, to be taught to new members as the correct way to perceive,
think and feel in relation to those problems.
Mijnd Huijser: A group’s set of shared norms and values expressed in the behaviour of the
group’s members.
Fons Trompenaars: Culture is the way in which a group of people solve problems.
Cultural Programming (e.g. that we decide to put food on a plate and eat it with fork and knife)
culture is learned through upbringing, socialisation, norms and values and perceptions
upbringing repeats things so often that we end up thinking it was normal (e.g. handshake)
socialisation teaches us through interaction with others
norms and values (e.g. giving your seat to elderly person on the bus)
through perception we make (un)conscious choices about how we want to behave
three levels of programming: individual, cultural, human nature
Culture and Subcultures
possible subcultures: continent, country, ethnic, regional, urban or rural, religion, social class,
gender, age, profession, hobby, corporate
it is good to be aware of differences as well as similarities and overlaps in our subcultures
Intercultural Communication
communication: exchange of meaning
illustration 1.3
Summary Intercultural Sensitivity – Anika Ochel 2
, Working with Hall’s Model of Cultural Differences
comparison of culture to a gigantic, finely tuned computer
communicating in a different culture setting is like working with a computer programme that
needs different action sequences
need of new tools to work with other programmes/cultures
Key concepts for more effective intercultural communication
Communication: high and low context
all communication takes place within a certain context
how much meaning is communicated through the context itself differs
distinguish high and low context communication, not better or worse
low context high context
most of message in person itself and context, not
information communicated
everything is spelled out explicitly but implicitly and
explicitly
often nonverbally
compartmentalising: structure large communities, access to networks, keep
information into segments individuals informed
information has clear structure,
less need for specific background information
but doesn’t flow very fast
starting with main point, ending
starting with context to get to main point
with details
misunderstanding caused by too little or too much context
too much information sound belittling, too little information is unclear
intercultural sensitivity means to be able to provide right amount of context
high and low context countries
not black and white opposites
may be overlap
high and low context subcultures
whole range of differences in need for context depending on regional, urban,
rural, ethnic, social class, professional, gender and generational subcultures
women communicate higher context than men, older generation prefer
higher context than young
Can we communicate high as well as low context? Yes, in changing strategy.
Summary Intercultural Sensitivity – Anika Ochel 3