FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT –
BMAN 311
CONTENT OF NOTES:
SU 1 – 9: CH 1,3,4,5 & 9, 7 & 17, 10, 13, 18, 15&16.
APPLICABLE THEORY & CALCULATIONS
GeekyS
CALCULATIONS ARE SHOWN USING A SHARP EL- 738 BUSINESS/
FINANCIAL CALCULATOR BMAN 311 NOTES AVAILABLE ON
STUVIA.CO.ZA
TEXT BOOK: MARX, J., DE SWART, C., BEAUMONT SMITH, M., &
ERASMUS, P. 2013. Financial Management: in Southern Africa. 4th
ed. South Africa: Pearson Education. 464 p.
,F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
STUDY UNIT 1: CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Financial management emphasizes on wealth
OUTCOMES: maximization rather than profit maximization. For a
Goal of financial management business, it is not necessary that profit should be the
Financial management and other subjects only objective; it may concentrate on various other
Functions of a financial manager aspects like increasing sales, capturing more market
Principles of financial management share etc, which will take care of profitability.
In wealth maximization, major emphasizes is on cash
flows rather than profit. So, to evaluate various
Introduction alternatives for decision making, cash flows are taken
Why do businesses exist? under consideration. For e.g. To measure the worth of
a project, criteria like: “present value of its cash inflow
• Satisfy human needs by providing a product/
– present value of cash outflows” (net present value)
service.
is taken. This approach considers cash flows rather
What is required to start a business?
than profits into consideration and also use
• Financing – Owners’ Equity / Loans discounting technique to find out worth of a project.
Business forms Thus, maximization of wealth approach believes that
• Sole proprietorship money has time value.
• Partnership A manager should align his/her objective to broad
• Companies objective of organization and achieve a trade-off
between risk and return while making decision;
keeping in mind the ultimate goal of financial
Economic principle management i.e. To maximize the wealth of its
What is the economic principle? current shareholders.
• Statement of inter-relationships among
economic factors that explains what may
cause what, or what may happen under
Basic management tasks
Planning
certain circumstances. Also called economic
Organising
law.
Activating / Leading
Importance in financial management
Control
• Handling of funds & Decision making
Functions of a financial manager
Goal of financial management Investment decisions
Long-term
Financing decisions
• Increase value of the firm
Ensuring Profitability
Short-term
Ensuring Positive cash flow
• Profitability
Ensuring Solvency
• Liquidity
• Solvency
Principles of financial management
Cost-benefit principle
Question The difference between Risk-return principle
Profitability / Wealth
Time-value-of-money principle
2
,F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
STUDY UNIT 2: CHAPTER 3
UNDERSTANDING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF A BUSINESS
The Classification of financial
OUTCOMES:
information
Users of financial statements Assets
Classification of financial information Liabilities
Income Statement Owners' Equity
Balance Sheet Revenues
Cash flow Statement Expenses
Users of financial statements: Financial statements:
Owners/Shareholders Income statement
Management Balance Sheet
Creditors Cash flow statement
labour unions
Investment analysts
The State Accounting Equation: [BEL]
Credit bureaus Assets = Owners' Equity + liabilities
INCOME STATEMENT
Nature Accounting period
• Provides a financial summary of • Refers to the period of time covered by an
performance during a period of time by income statement; month, quarter of a
comparing revenue and expenses. year, half a year or yearly.
Purpose AKA earnings statement, statement of
• To evaluate the profitability of a firm, operations, and profit/ loss statement.
Example of an Income Statement (condensed)
3
, F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
Example
Complete the Income Statement
Sales 800 000 Interest expense 25 000
Gross profit 450 000 Income tax 50 000
Operating profit 140 000
Income statement Income statement
Sales (Net) 800 000 Sales (Net) 800 000
Less: Cost of goods sold Less: Cost of goods sold 350 000
Gross profit 450 000 Gross profit 450 000
Less: Operating expenses Less: Operating expenses 310 000
Operating Profit 140 000 Operating Profit 140 000
Interest Income - Interest Income -
Earnings before Interest and Tax (EBIT) Earnings before Interest and Tax (EBIT) 140 000
Less: Interest Expenses 25 000 Less: Interest Expenses 25 000
Earnings before tax (EBT) Earnings before tax (EBT) 115 000
Less: Tax 50 000 Less: Tax 50 000
EARNINGS AFTER TAX (EAT) EARNINGS AFTER TAX (EAT) 65 000
BALANCE SHEET
Purpose of balance sheet
• To show the financial position of a business at a particular date
Three elements of a balance sheet
• Assets – Fixed and Current assets
• Owners’ equity (Shareholders equity) – Resources invested by owners
• Liabilities – Long term liabilities and current liabilities
AKA Statement of financial position
Example of old fashioned Balance sheet:
4
,F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
Example of a modern format - Balance Sheet:
EMPLOYMENT OF CAPITAL
Non-current assets
Fixed assets :- Buildings, Land, Vehicles, Equipment 16 980 400
Current assets 7 090 100
Inventories 1 600 000
Accounts receivable 4 800 020
Cash 690 080
Employment of capital (Total Assets) 24 070 500
CAPITAL EMPLOYED
Shareholders’ Equity 20 870 500
Ordinary share capital 12 000 000
Retained income 7 870 500
Preference share capital 1 000 000
Non-current liabilities 2 400 000
Mortgage bond 2 400 000
Current liabilities 800 000
Capital employed 24 070 500
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
Cash Flow Cash inflow Cash outflow
Movement of cash in and out of Increase cash in business Decrease cash in business
business
Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow from operating activities
Cash flow from investing activities
Cash flow from financing activities
Operating activities Investing activities Financing activities
Income statement Assets Equity, Liabilities
• Cash receipts from sales • Cash inflow from the sale • Cash inflow from: issuing
• Cash paid to suppliers and of property, plant and shares, mortgages and
employees equipment long term and short term
• Collection of loans made to loans
other • Cash outflow from:
• Cash outflow when cash payment of loans/ equity
paid to purchase property, holders
plant or equipment
5
, FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
F
Example of Cash Flow Statement
CASH FLOW STATEMNT FOR THE YEAR ENDED 20**
Cash flows from operating activities 226 480
Cash receipts from customers 9 199 980
Cash paid to suppliers and employees (7 403 000
Cash generated from operations *1 1 796 980
Interest received -
Interest paid *3 (26 000
Dividends Received -
Dividends paid *4 (532 000
Taxation Paid *5 (1 012 500
Cash flows from investing activities (836 820
Purchase of non-current assets (860 820
Proceeds from non-current assets 24 000
Cash flows from financing activities 1 200 000
Proceeds from the issue of share capital 1 000 000
Proceeds from long-term borrowings 200 000
Net change in cash and cash equivalents *2 589 660
Cash and cash equivalents: beginning of year 100 420
Cash and cash equivalents: end of year *2 690 080
PAYMENTS OF DIVIDENDS AND INTEREST ARE NOT REGARDED AS FINANCING ACTIVITIES
Exercises:
Accounts payable Inventories Expenses OUTFLOWS
2010 - R 250 000 2010 R 220 000 Interest expense
2011 - R 230 000 2011 R 200 000 Tax
Influence on cash Outflow Influence on cash Inflow Operating expenses
of R 20 000 (Accounts payable of R 20 000 (Inventories
decrease) decrease)
Accounts receivable Fixed assets Income INFLOWS
2010 R 200 000 2010 R 9 800 000 Interest income
2011 R 190 000 2011 R 9 950 000
Influence on cash Inflow of Influence on cash Outflow
R 10 000 (Accounts receivable of R 150 000 (Fix assets
decrease) increase)
6
,F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
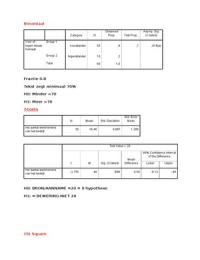
OPDRAG 1 / ASSIGNMENT 1
Voltooi die Inkomstestaat / Complete the Income Statement
Verkope / Sales 1000 000
Bruto wins / Gross profit 300 000
Bedryfsuitgawes / Operating expenses 150 000
Langtermynlening @10% per jaar / Long-term debt @ 10% per annum 400 000
Belastingkoers / Tax rate 40%
OPDRAG 2 / ASSIGNMENT 2
Voltooi die balansstaat / Complete the balance sheet
Gewone aandelekapitaal / Ordinary share capital 12 000 000
Behoue inkomste / Retained income 8 870 500
Verbandlening / Mortgage bond 2 400 000
Rekeninge betaalbaar / Accounts payable 800 000
Grond en geboue / Land and buildings 8 490 200
Masjinerie en aanleg / Machinery and plant 7 252 200
Voertuie / Vehicles 1 538 000
Opgehoopte depresiasie / Accumulated depreciation 300 000
Kontant / Cash 690 080
Rekeninge ontvangbaar / Accounts receivable 4 800 020
Voorrade / Inventory 1 600 000
7
, F FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – BMAN 311 STUVIA.CO.ZA
OPDRAG 3 / ASSIGNMENT 3
Voltooi die Inkomstestaat / Complete the Income Statement
Koste van verkope / Cost of sales 500 000
Bruto wins / Gross profit 800 000
Bedryfsuitgawes / Operating expenses 140 000
Langtermynlening @12% per jaar / Long-term debt @ 12% per annum 600 000
Belastingkoers / Tax rate 40%
OPDRAG 4 / ASSIGNMENT 4
Voltooi die balansstaat / Complete the balance sheet
Gewone aandelekapitaal / Ordinary share capital 2 500 000
Behoue inkomste / Retained income 700 000
Verbandlening / Mortgage bond 700 000
Rekeninge betaalbaar / Accounts payable 400 000
Totale kapitaal aangewend / Total capital employed 4 300 000
Grond en geboue / Land and buildings 700 000
Masjinerie en aanleg / Machinery and plant 1 400 000
Voertuie / Vehicles 600 000
Opgehoopte depresiasie / Accumulated depreciation 200 000
Kontant / Cash 300 000
Rekeninge ontvangbaar / Accounts receivable 900 000
Voorrade / Inventory 600 000
8