Samenvatting
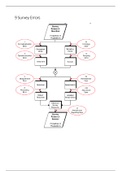
Summary 9 Survey Errors
- Instelling
- Tilburg University (UVT)
If you mail me you'll get this for 1 euro. The 9 survey errors are explained by Rik Pieters throughout the whole course. I tried to put all information I could find together in 1 document. It personally helps me to understand the errors better, since the one-line explanations are quite vague.
[Meer zien]