Grade 12 Macroeconomics Short Summary
Circular Flow of Economic Activity:
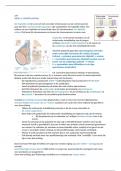
• The circular flow of economic activity is a visual representation of how goods, services, and
money flow through an economy.
• It shows how households and firms interact with one another and how their decisions
impact the overall economy.
• In the circular flow model, households are the source of all demand for goods and services,
as they purchase goods and services from firms.
• Firms, in turn, use the revenue they receive from households to pay for the resources they
need to produce goods and services, such as labour, capital, and raw materials.
• These resources are supplied by households, who earn income in the form of wages,
salaries, rent, interest, and profits.
• The circular flow model highlights the interdependence of households and firms and the role
that market transactions play in the economy.
Business Cycles:
• Business cycles are the fluctuations in economic activity that occur over time.
• The cycles typically last several years and are characterized by periods of expansion
(growth), peak (the highest point of economic activity), contraction (recession), and trough
(the lowest point of the cycle).
• Business cycles are driven by various factors such as changes in consumer spending,
investment, and government policies.
• For example, a decrease in consumer spending can lead to a decrease in demand for goods
and services, causing businesses to reduce production and employment.
• This, in turn, can further decrease consumer spending and lead to a recession.
• On the other hand, an increase in investment can lead to increased production and
employment and drive the economy towards growth.
• Understanding business cycles is important for policymakers, as they can use monetary and
fiscal policies to mitigate the impact of recessions and promote economic growth.
Public Sector:
• The public sector is an important component of the economy, and includes all government
agencies, departments, and state-owned enterprises that provide goods and services to the
public.
• The public sector plays a vital role in promoting economic stability and growth by providing
public goods and services, such as healthcare, education, and defence, and by collecting
taxes to fund these services.
• The public sector also plays a significant role in regulating the economy, by setting and
enforcing rules and regulations that promote economic stability and protect the welfare of
citizens.
Circular Flow of Economic Activity:
• The circular flow of economic activity is a visual representation of how goods, services, and
money flow through an economy.
• It shows how households and firms interact with one another and how their decisions
impact the overall economy.
• In the circular flow model, households are the source of all demand for goods and services,
as they purchase goods and services from firms.
• Firms, in turn, use the revenue they receive from households to pay for the resources they
need to produce goods and services, such as labour, capital, and raw materials.
• These resources are supplied by households, who earn income in the form of wages,
salaries, rent, interest, and profits.
• The circular flow model highlights the interdependence of households and firms and the role
that market transactions play in the economy.
Business Cycles:
• Business cycles are the fluctuations in economic activity that occur over time.
• The cycles typically last several years and are characterized by periods of expansion
(growth), peak (the highest point of economic activity), contraction (recession), and trough
(the lowest point of the cycle).
• Business cycles are driven by various factors such as changes in consumer spending,
investment, and government policies.
• For example, a decrease in consumer spending can lead to a decrease in demand for goods
and services, causing businesses to reduce production and employment.
• This, in turn, can further decrease consumer spending and lead to a recession.
• On the other hand, an increase in investment can lead to increased production and
employment and drive the economy towards growth.
• Understanding business cycles is important for policymakers, as they can use monetary and
fiscal policies to mitigate the impact of recessions and promote economic growth.
Public Sector:
• The public sector is an important component of the economy, and includes all government
agencies, departments, and state-owned enterprises that provide goods and services to the
public.
• The public sector plays a vital role in promoting economic stability and growth by providing
public goods and services, such as healthcare, education, and defence, and by collecting
taxes to fund these services.
• The public sector also plays a significant role in regulating the economy, by setting and
enforcing rules and regulations that promote economic stability and protect the welfare of
citizens.