Summary
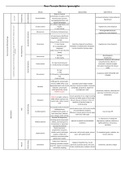
Summary Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs and Spasmolytics pharmacology table
- Course
- Pharmacology
- Institution
- University Of The Witwatersrand (wits)
Looking for comprehensive study notes to help you prepare for your exams on neuromuscular blocking drugs and spasmolytics? Look no further! Our study notes provide an easy-to-understand and well-organized format, presented in a convenient table that will save you time and effort in your studies. ...
[Show more]